Program Overview
The CEIPI IP Business Academy’s Open Foresight Program Board’s Tasks
Strategic Direction
The Board should determine the strategic direction of the program and ensure that it meets the needs of participants and the IP community.
Topic identification
It should identify relevant topics and trends in the field of IP management that are of interest to participants.
Expert contributions
The board can invite experts from different fields to lead lectures, workshops or discussions to expand the knowledge of the participants.
Quality control
It should monitor the quality of the content provided and ensure that it meets the high standards of the CEIPI.
Networking
It can create opportunities for participants to network to promote knowledge sharing and collaboration.
Promote ISO56006 / DIN77006 standards
The Board should ensure that the implementation of these standards is taken into account in the program.
Feedback and improvement
The board should collect feedback from participants and make improvements to the program based on this.
What is the program about?
The CEIPI IP Business Academy operates an open foresight program to give all stakeholders of this information, learning and training platform the opportunity to jointly develop, share and use future knowledge about IP management. We support companies, institutions, law firms and professionals through academic teaching as well as through the provision of learning management systems for the systematic implementation of the ISO56006/DIN77006 standards. It is important for the conformity of IP management to anticipate future developments and to react individually and appropriately.
IP issues as part of individual and corporate top-level strategy
The open foresight program of the CEIPI IP Business Academy is not about making clear predictions and forecasts about the future of IP management. Rather, it is about generating and prioritizing relevant developments in the field of IP and IP management in the areas of:
- Legal Framework
- Social
- Technology
- Markets
represent value for the stakeholders of the CEIPI IP Business Academy and the operators and users of our LMS. From personal career planning to corporate planning to the design of national IP strategies, an understanding of future IP management topics is relevant and helpful.
The early recognition of changes implies a knowledge advantage that enables organizations and individuals to prepare for changes earlier than competitors to the resulting opportunities. Organizations can draw adequate strategic and organizational conclusions at an early stage and skim off the potential that crystallizes. Accordingly, strategic foresight enables the generation of specific time advantages for the career and strategy of professionals, experts and organizations. It should be stressed that the essence of our foresight program is not to develop an accurate forecast, but is focused on the improvement of the foresight capabilities of the users to anticipate and deal with change. This means achieving an improved understanding of the major issues that arises for IP management to deal with in the long term.
Objectives of the Open Foresight Program
Important objectives of our open foresight program for IP management are:
- Predicting new skills that will be required by IP experts
- Recognizing developments that could (disruptively) change previous business activities
- Dealing with problems and challenges at a time when they are easier to solve
- Expanding knowledge of opportunities and risks
- Identifying of drivers and their possible effects and perspectives
- Developing desirable and less desirable futures
- Starting and stimulating ongoing discussion processes
- Developing possible new ideas and strategic options
- Developing content and training to help users deal with dynamic environments
- Detecting discontinuities, changes and weak signals
- Securing competitiveness for the future
- Creating sustainable innovation potential
- Generating of new know-how for the development of new business areas
Organization: The institutionalized Open Foresight Model
The open foresight program of the CEIPI IP Business Academy is operated as an institutionalized model in an iterative process scheme. The advisory board of the open foresight program works as a network to provide the necessary expertise. The addition of the inputs takes place continuously. The aim is to obtain qualitative information about the future, as well as to obtain priority assessments.
In addition, this expert network of the advisory board also discusses and debates about IP and IP management relevant future issues. This early enlightenment is linked to the intention of anticipating future developments and events. In this sense, these developments are processed systematically and consistently and made available to individuals, companies, and institutions.
The institutionalized open foresight model pursues the following goals:
- The foresight program as an expert network and the integration of a larger number of participants with different knowledge and skills provides a wide variety of new insights and may call into question existing assumptions about, for example, future customer needs, business models, technological or other environmental developments.
- Through open foresight activities, the stakeholders of the CEIPI IP Business Academy are made more aware of possible future developments and weak signals.
- At the same time, tolerance for the need for continuous training should be increased.
- The open foresight program offers the opportunity to get to know the knowledge, skills and interests of the different partners. This represents an optimal basis for the qualification of possible partners for later professional cooperation.
- The open foresight program serves to uncover “blind spots” about future developments in relation to external partners.
- By integrating a network of experts into the Open Foresight program, important input from outside is taken into account and common images of the future are created. This can strengthen the relationship between them and optimize the basis of trust. At the same time, the commitment can be increased, the chance for a later implementation of standard-compliant IP management on the basis of learning management systems improved and the foresight process will be made more effective
Open Foresight Process
The open foresight process used at the CEIPI IP Business Academy is based on the early detection system of the Battelle Institute (Frankfurt am Main, Germany). It is a combination of a linear phase model that is carried out in iterative cycles on an annual basis. The following objectives are thereby pursued:
- Gaining time to prepare for new social, political and technological conditions and to further expand own competitive advantages
- Risk minimization, especially for long-term investment decisions
- Earlier and safer choices in responding to social and political, normative and regulatory demands
The open foresight process used is based on the following assumptions:
- Social, political and technological changes do not happen by chance, but are “made” by people and guided by human interests.
- Underlying change are certain mechanisms of development and relatively stable patterns of diffusion.
- Changes in the company’s environment are triggered by events and supported by pioneers.
The linear part of the open foresight process is carried out according to Horton (Horton, A. (1999), “A simple guide to successful foresight”, Foresight, Vol. 1 No. 1, pp. 5-9.), with three phases of the process that can be distinguished:
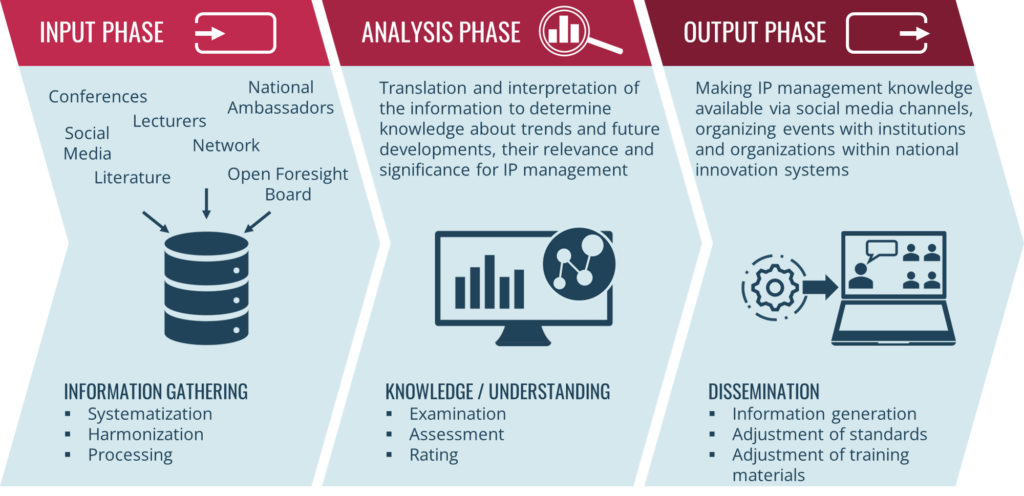
Phase1 – Collecting inputs:
Phase 1 involves gathering, comparing and summarizing available information such as trends, expected developments, brainstorming about unusual occurrences and lessons learned from the material processed. Sources for this are the experts of the advisory board of the open foresight program, literature review, conferences and events, social media analysis.
Phase 2 – Foresight:
Phase 2 involves the translation and interpretation of this knowledge in order to gain an understanding of what this will mean for IP and IP management. For this purpose, the information collected is analysed. The aim is to identify the central implications for the future.
Phase 3 – Outputs and action:
In step 3, the findings are integrated and evaluated with the aim of achieving concrete results for the stakeholders of the CEIPI IP Business Academy and the operators and users of the learning management systems for the implementation of standard-compliant IP management.
Based on the findings of the open foresight process, various information and learning opportunities are developed and offered via the CEIPI IP Business Academy. These include the following offers
- Information about the findings about the social media channels of the CEIPI IP Business Academy, via the blog www.ipbusinessacadey.org and on LinkedIn
- Seminar events with national and regional institutions in the innovation systems.
- Teaching content for the academic training programs on IP management
- Content for the learning management systems
The aim is that the expectations and needs of the stakeholders are taken into account in these outputs in order to maintain the motivation for continuous further training in the field of IP management.
The open foresight process allows each phase to generate greater value than the previous one through the increase of information for the know-how building of the CEPI IP Business Academy stakeholders.
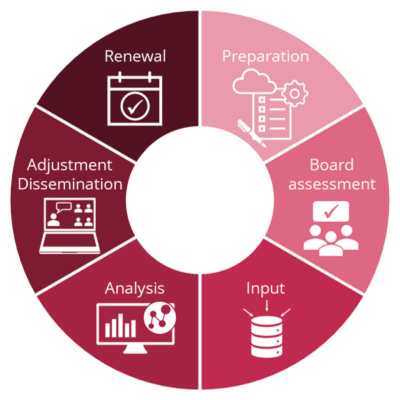
This linear part of the open foresight process of the CEIPI IP Business Academy is embedded in a cycle according to Ian Miles (Miles, I. (2012), “Dynamic foresight evaluation”, Foresight Vol. 14 No. 1, pp. 69-81). A process with five different activities is carried out in the annual cycle.
- Pre Foresight: Scoping – based on the existing results of the last Foresight cycle, the most relevant topics are focused on
- Recruitment: new appointments to the board, involvement of individual experts
- Generation: Intelligence Gathering, Knowledge Fusing, Visioning, Targeting, Synthesis
- Action: dissemination, implementation
- Renewal: Beginning of the new cycle
.
Result
A fundamental objective in strategic early detection is to identify signals for new developments as early as possible, which can be interpreted as signs of latent opportunities or risks. For this purpose, a radar display with different sectors is published. The representation corresponds to a scanning and rastering of the environment, in order to seize and represent future developments and influences. The sectors correspond to different thematic areas. Trends closer in time are positioned closer to the origin in the trend radar, long-term developments are positioned in the outer areas of the radar.
Scanning, i.e. searching for new influences and events, is supplemented by monitoring. If scanning has provided an indication of a relevant phenomenon, the next step is to search for additional information on this phenomenon. This process is called monitoring and refers to the in-depth and permanent observation of this phenomenon. Thus, the radar not only takes into account new phenomena with a relevant influence on standard-compliant IP management, but also monitors and displays their development.



