Design Thinking and IP Design: Generating and Protecting Digital Innovation
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the intersection of design thinking and intellectual property (IP) design has become increasingly crucial for businesses seeking to innovate and protect their digital assets. This blog post explores the concept of design thinking, its application in IP design, and the importance of using IP design for digital objects to generate patentable solutions.
Understanding Design Thinking
Design thinking is a non-linear, solution-based innovation framework that puts users at the center of the problem-solving process. This human-centered approach encourages empathy, creativity, and iterative problem-solving to develop innovative solutions that meet user needs.
- Innovation must be novel and useful. This concept emphasizes that truly innovative solutions should not only be original and creative but also provide practical value and address real-world problems effectively.
- Innovation is a continuous iterative process, as there is always a better solution to a problem. This principle underscores the importance of ongoing refinement and improvement, recognizing that innovation is not a one-time event but a cyclical journey of learning and adaptation.
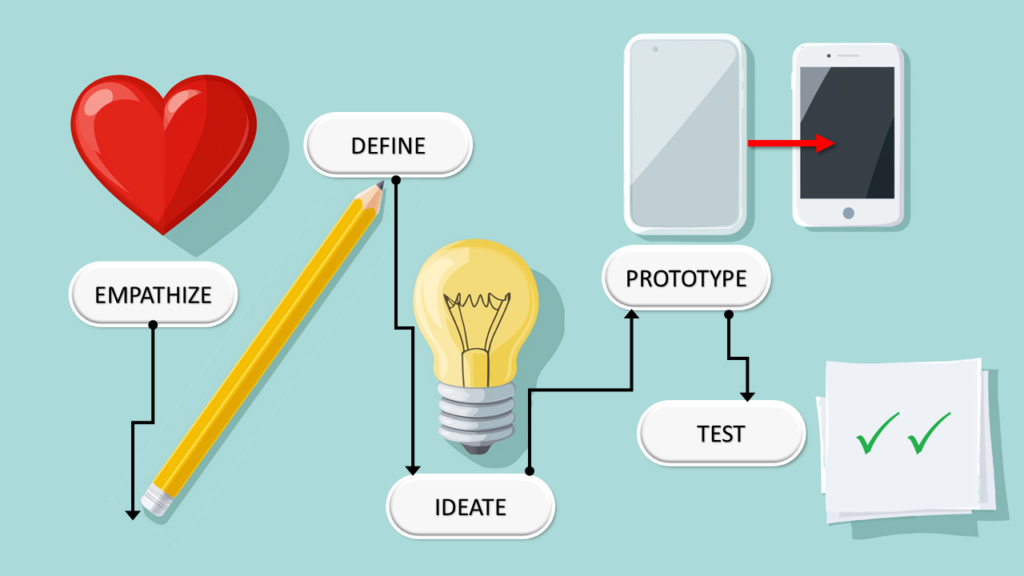
The design thinking process typically involves five stages:
- Empathize: In this initial stage, designers immerse themselves in the user’s world, observing, engaging, and empathizing with their experiences to gain deep insights into their needs, challenges, and motivations.
- Define: The Define stage involves synthesizing the insights gathered during empathy work to articulate a clear, actionable problem statement that guides the rest of the design process.
- Ideate: During Ideation, teams generate a wide range of creative ideas, focusing on quantity over quality, to explore innovative solutions to the defined problem.
- Prototype: Prototyping involves creating tangible representations of potential solutions, allowing designers to explore and test ideas quickly and cost-effectively.
- Test: In the final stage, designers rigorously evaluate the prototypes with real users, gathering feedback to refine and improve the solution iteratively.
These stages are not necessarily sequential and can be repeated or conducted concurrently to gain deeper insights and develop more innovative solutions.
The Importance of IP Design
Intellectual Property (IP) design is the strategic creation, development, and management of intellectual property assets, including patents, trademarks, designs, copyrights, and trade secrets. As businesses undergo digital transformation, the role of IP design becomes increasingly critical for several reasons:
- Protection of Innovations
IP design ensures that digital innovations, such as software algorithms or user interfaces, are legally protected, preventing competitors from replicating or exploiting them without authorization. This protection fosters a secure environment for businesses to invest in and develop groundbreaking ideas without fear of infringement. - Competitive Advantage
By securing IP rights, companies can differentiate themselves from competitors, creating a unique market position that is difficult to replicate. This exclusivity not only enhances brand value but also provides a strategic edge in the ever-evolving digital economy. - Value Creation
Effective IP design increases the value of products and services by establishing legal barriers to entry for competitors and enabling premium pricing. Additionally, businesses can monetize their IP through licensing agreements or partnerships, unlocking new revenue streams. - Risk Management
IP design involves identifying potential risks, such as infringement or disputes, and implementing strategies to mitigate them. Proactively managing these risks ensures that businesses can navigate the competitive landscape with confidence and avoid costly legal challenges. - Market Positioning
Leveraging IP strategically allows businesses to enhance their reputation and differentiate their offerings in the marketplace. This differentiation not only attracts customers but also strengthens the company’s overall market presence and long-term growth potential.
Applying Design Thinking to IP Design
The application of design thinking principles to IP design can lead to more innovative and user-centric intellectual property strategies. Here’s how the design thinking process can be applied to IP design:
- Empathize
In this stage, IP designers should focus on understanding the needs of both the business and its users. This involves: -
- Conducting user research to identify pain points and opportunities
- Analyzing market trends and competitor activities
- Gathering insights from various stakeholders within the organization
- Define
Based on the insights gathered, IP designers can define the specific IP challenges and opportunities. This might include:
-
- Identifying key areas of innovation that require protection
- Defining the scope of IP protection needed for digital objects
- Clarifying the business objectives that IP strategy should support
- Ideate
This stage involves generating a wide range of potential IP strategies and solutions. Techniques might include:
-
- Brainstorming sessions with cross-functional teams
- Exploring various types of IP protection (patents, trademarks, copyrights, etc.)
- Considering non-traditional IP strategies that align with digital innovation
- Prototype
In the context of IP design, prototyping might involve:
-
- Drafting preliminary patent applications
- Creating mock-ups of digital objects with potential IP protection
- Developing sample IP portfolios for different business scenarios
- Test
Testing in IP design could include:
-
- Conducting freedom-to-operate analyses
- Evaluating the strength of potential IP claims
- Assessing the market response to protected digital innovations
IP Design for Digital Objects
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, applying IP design to digital objects has become a critical strategy for businesses to protect their innovations and maintain a competitive edge. As companies invest heavily in digital assets such as use cases, business models, and customer journeys, the need for robust IP protection has never been more pressing. Here’s why IP design for digital objects is crucial in the modern digital economy:
Protection of Intangible Assets
Digital objects represent significant investments in time, resources, and innovation, making them valuable intangible assets for businesses. IP design provides a framework for safeguarding these digital creations from unauthorized use or replication. By implementing effective IP protection strategies, companies can secure their digital innovations and preserve their competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Securing Competitive Advantage
Patenting unique digital processes, user interfaces, or algorithms allows businesses to establish and maintain a strong position in the digital marketplace. This exclusivity enables companies to differentiate themselves from competitors and create barriers to entry for potential rivals. By leveraging IP design, organizations can protect their innovative digital solutions and ensure they remain at the forefront of their industry.
Facilitating Digital Transformation
As businesses undergo digital transformation, IP design plays a crucial role in protecting new digital innovations and encouraging further technological advancements. By ensuring that digital assets are properly protected, companies can confidently invest in and develop cutting-edge solutions. This protection fosters a culture of innovation and drives continuous improvement in digital products and services.
Monetization Opportunities
Well-designed IP for digital objects can open up new revenue streams through licensing or partnerships.
Generating Patentable Solutions for Digital Objects
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, creating patentable solutions for digital objects has become crucial for businesses seeking to protect their innovations and maintain a competitive edge. By focusing on specific strategies, companies can develop unique digital assets that meet the criteria for patent eligibility. Here are five key approaches to consider:
- Focus on Technical Solutions
Technical solutions that address specific problems in digital environments offer a promising avenue for patentability. These solutions often involve innovative algorithms or processes that significantly enhance the efficiency or functionality of digital systems. For instance, a novel algorithm that optimizes data compression in cloud storage could be a strong candidate for a patent. - Identify Novel User Interactions
Innovative user interaction methods can open up new possibilities for patentable digital objects. These interactions might involve unique gesture recognition systems for touchscreen devices or advanced voice-controlled processes that revolutionize how users engage with digital interfaces. Such innovations can significantly enhance user experience and provide a strong basis for patent applications. - Develop Unique Data Processing Methods
In today’s data-driven world, innovative approaches to data processing can yield valuable intellectual property. Novel methods for collecting, analyzing, or visualizing big data can offer significant advantages in various industries. These unique data processing techniques, when properly developed and documented, can form the basis of strong patent applications. - Create Innovative Business Methods
While business methods themselves may be challenging to patent, their technical implementations in digital environments can often qualify for patent protection. This strategy involves developing unique digital systems or processes that enable new ways of conducting business operations. For example, a sophisticated AI-driven customer service platform that significantly improves response times and accuracy could be patentable. - Design Novel System Architectures
Innovative system architectures that offer unique solutions to digital challenges can be prime candidates for patents. These architectures might involve new ways of structuring cloud computing systems, distributed networks, or IoT ecosystems. By focusing on novel approaches to system design that solve specific technical problems, businesses can create patentable digital assets that provide long-term competitive advantages.
Examples of IP Design in Action
Let’s explore some real-world examples of how companies have successfully applied IP design to protect their digital innovations:
Uber’s Dynamic Pricing Algorithm: Uber’s patented surge pricing algorithm is an example of IP design applied to a digital business model. This system automatically adjusts ride prices based on real-time supply and demand, optimizing both driver availability and passenger wait times.
Netflix’s Recommendation Engine: Netflix’s recommendation system, which suggests content to users based on their viewing history and preferences, is protected by multiple patents. This IP design strategy has been crucial in maintaining Netflix’s competitive edge in the streaming market.
Starbucks’ Mobile Ordering System: Starbucks has patented various aspects of its mobile ordering system, including methods for customizing orders, managing queue times, and integrating with in-store operations. This IP design strategy has helped Starbucks maintain its leadership in digital customer experience within the food and beverage industry.
GE Healthcare’s Adventure Series: GE Healthcare’s Adventure Series, which redesigned MRI machines to be more child-friendly, is an excellent example of design thinking applied to product development. While not explicitly an IP design case, it demonstrates how user-centric innovation can lead to patentable solutions in hardware and software interfaces.
Conclusion
As businesses continue to innovate in the digital realm, the integration of design thinking and IP design becomes increasingly vital. By applying design thinking principles to IP strategy, companies can create more user-centric, innovative, and legally protected digital assets. This approach not only safeguards investments in digital innovation but also creates new opportunities for growth and competitive advantage.
The key to successful IP design for digital objects lies in understanding the unique challenges and opportunities presented by the digital landscape. By focusing on technical solutions, novel user interactions, and innovative system architectures, businesses can generate patentable solutions that protect their digital innovations.
As we move further into the digital age, those companies that master the art of IP design for digital objects will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive and innovation-driven marketplace. By embracing this approach, businesses can ensure that their digital innovations are not only groundbreaking but also well-protected, paving the way for sustainable growth and success in the digital economy.
About the author
 Christian Barske studied mechanical engineering with emphasis on automotive technology at the Technische Hochschule Hamburg-Harburg and the Technical University Munich. He graduated with a diploma thesis about solutions of production problems in the automotive industry. He began to work in the field of intellectual property rights in 2008. After his training as a Patent Attorney at KRAMER BARSKE SCHMIDTCHEN, the Patent Senate of the Higher District Court in Duesseldorf, the German Patent and Trademark Office and the Federal Patent Court, he was registered as a German Patent Attorney in 2011 and as a European Patent Attorney in the following year.
Christian Barske studied mechanical engineering with emphasis on automotive technology at the Technische Hochschule Hamburg-Harburg and the Technical University Munich. He graduated with a diploma thesis about solutions of production problems in the automotive industry. He began to work in the field of intellectual property rights in 2008. After his training as a Patent Attorney at KRAMER BARSKE SCHMIDTCHEN, the Patent Senate of the Higher District Court in Duesseldorf, the German Patent and Trademark Office and the Federal Patent Court, he was registered as a German Patent Attorney in 2011 and as a European Patent Attorney in the following year.
Since 2014 Christian Barske is a partner of KRAMER BARSKE SCHMIDTCHEN. He assists especially German and Japanese clients. In close cooperation and also supported by his training as a business mediator, he recognizes the clients needs and realises their goals.