Why are IP management standards so important for companies?
Industry 4.0, AI and the Internet of Things are forcing companies to radically rethink how they manage intellectual property. Companies are developing new business models, use cases and applications with significant digital components, such as smart platforms, 5G communication standards, cloud computing, artificial intelligence and digital twins. And companies are seeking to legally protect their service offerings by patenting their technical developments and designing patent portfolios that are specifically focused on customer value. Intellectual property is, therefore, an important concept in the technological and economic field related to Industry 4.0 and IoT. However, digital patents are different. They do not come from physical reality or technical functionality, but from the application, the solution or the use case. This also affects the analysis of the competitive situation, including third party patents that need to be taken into account.
In such a technical environment, freedom-to-operate searches are very extensive and time-consuming, or almost impossible. The large patent portfolios of third parties pose considerable dangers and liability risks, for example in the use of telecommunications technologies in new products. Failure to comply with the intellectual property rights of third parties can result in severe sanctions, such as sales bans or claims for damages, making the identification and consideration of third party patents an essential element of loss prevention.
IP Management Standards, such as ISO 56005 and DIN 77006, are designed to help companies and IP service providers develop their abilities to handle the challenges of modern and compliant IP management. They focus on leadership and strategy, tools and methods.
ISO 56005 Innovation management—Tools and methods for intellectual property management
ISO 56005 is part of a family of standards focused on innovation management. The ISO family of standards aims to provide tools and methods that can be used to implement a holistic approach to innovation management, including appropriate stakeholder interaction in the innovation process.
The ISO family of standards provides for a framework to support innovation management procedures starting from the idea, via research and development, up to the IP creation and verified products or services. ISO 56005 is designed as a guideline to systematically manage IP within the innovation environment. It supports the innovation process and provides an IP strategy which is aligned with the business strategy including 5 major activities and outcomes to help organizations protect their best ideas: IP landscaping, IP creation and acquisition, IP portfolio, IP commercialization and IP risk management.
The ISO 56005 standard can be used for any type of innovation activities. It defines different tasks and responsibilities for IP management. These include, for example
- Defining the innovation results to be protected and the appropriate resources to manage this intellectual property;
- Monitoring third party IP rights to identify opportunities and risks as input for innovation activities and to avoid potential infringement of third party rights; and last but not least
- Awareness raising and, where necessary, training within the organization.
The appendix to ISO 56005 provides an overview of checklists, tools and methods for invention identification and disclosure, IP generation, acquisition and maintenance, IP research, IP rights assessment and IP risk management, as well as a collection of best practice instructions and strategies for the systematic management of intellectual property in the innovation environment.

DIN 77006 Intellectual property management systems – Requirements
DIN 77006 is a German standard. It is important to understand that it is part of the ISO 9000/9001 family of standards, which deals with the design and implementation of management systems. DIN 77006 sees the proper handling of IP as a management task and does not focus on innovation management. It is important to note that the two standards do not contradict each other. Rather, it can be said that DIN 77006 is a more specific and stringent standard than ISO 56005.
The standard is open to almost any type of business model. It defines various requirements and tasks that need to be considered when implementing the standard. If a company wants to declare its conformity with DIN 77006, all relevant requirements for the specific business model must be fulfilled. Exceptions are possible if certain requirements cannot be applied by the organization or if the performance of a specific task is not relevant in an organization. For example, if a patent attorney does not generate his own IP, he describes his organization only to the extent that IP services are provided. The requirements for IP generation, for example, can then be excluded.
The High-Level-Structure of DIN77006
As mentioned above, DIN 77006 is part of the ISO9000/9001 family of standards. All standards in this family follow the same logic and structure. This uniform overarching structure of the standards is called a high level structure. Because the structures are always the same, new areas such as IP management can be efficiently integrated into the management system of an organization that has already implemented other standards in the ISO9000/9001 family.
In DIN 77006, the individual areas of the high-level structure are supplemented where necessary and specified with regard to IP and IP management. The appendix to the standard contains helpful explanations, examples and comments on almost every chapter of the requirements.

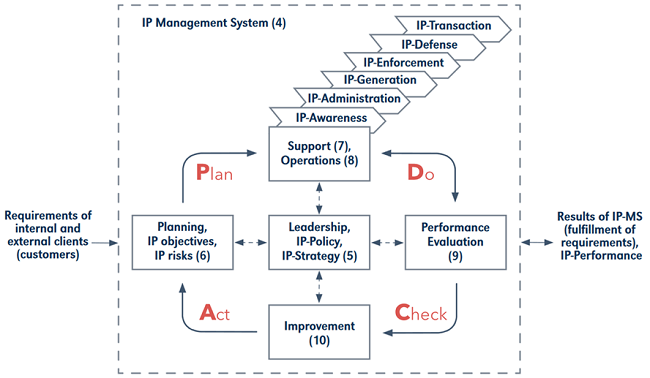
Process model of DIN77006 and ISO 9001 family
In addition to the common high-level structure, the ISO9000/9001 family of standards is based on a process model that implements the PDCA cycle. PDCA stands for Plan, Do, Check and Act. The concept behind the process model is that if the cycle is carried out continuously, there will be steady improvement in the quality of the management system.
From this point of view, IP management is an iterative process.
- Planning involves the definition of specific IP management objectives and the handling of the identified IP risks.
- The corresponding processes are then carried out as part of operations or support. This concerns the topics of IP awareness, IP administration, IP generation, IP enforcement, IP defense and IP transactions.
- The performance and effectiveness of the IP management system shall be regularly reviewed and recorded through IP reporting.
- Depending on the results of these reviews, a decision must be made as to whether and where the IP management system needs to be improved.
Summary
In summary, DIN 77006 helps an organization to establish an efficient and legally secure IP management system. As a result, for example, the organization’s compliance requirements are identified, understood and continuously met by all departments or members of the organization. Documentation requirements across all hierarchical levels and processes ensure that all relevant legal and regulatory requirements are met and that processes are optimally integrated to achieve business objectives.


