Innovation and Its Impact
Innovation is the backbone of modern business and societal development. It involves introducing new ideas, methods, products, or services that create significant improvements or advancements within an organization or industry. This process not only drives business growth but also plays a crucial role in addressing global challenges such as climate change and technological advancements. In this blog post, we will explore why innovation matters, its impact across various sectors, and specific examples from the energy market, CO2 emissions regulation, and the technological shift in mobile communications, as well as the deregulation of the telecom industry. Here are some important points why innovation is important:
Why Innovation Matters
Innovation plays a multifaceted role in driving business success, impacting various aspects of an organization from its competitive positioning to employee satisfaction. By understanding the key benefits of innovation, businesses can harness its power to enhance their operations, expand market opportunities, and foster a culture of creativity and growth.
- Competitive Advantage
Innovation allows companies to differentiate themselves from competitors by offering unique products or services, attracting more customers and building brand loyalty. This differentiation can lead to a strong market presence, where customers prefer the innovative company over others due to its unique offerings. By consistently innovating, companies can maintain a competitive edge that is difficult for competitors to replicate, ensuring long-term success. - Adaptation to Change
It enables businesses to adapt quickly to changes in technology, market trends, and consumer preferences, ensuring they remain agile and competitive. This adaptability is crucial in today’s fast-paced business environment, where companies that fail to adapt risk being left behind by more agile competitors. By embracing innovation, businesses can respond effectively to shifts in the market, ensuring they stay relevant and continue to grow. - Revenue Growth
Introducing innovative products or services can open up new revenue streams and expand market opportunities. This expansion can lead to increased market share and higher profitability, as innovative offerings often command premium prices due to their unique value proposition. Moreover, innovation can help companies enter new markets or segments, further diversifying their revenue base and reducing dependence on traditional products. - Cost Efficiency
Innovation involves finding more efficient ways to operate, which can lead to cost savings and improved productivity. By streamlining processes and leveraging technology, companies can reduce waste and optimize resource allocation, leading to significant cost reductions. Additionally, innovative solutions can automate tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic and creative work, thereby enhancing overall productivity. - Employee Satisfaction
Encouraging innovation fosters a culture of creativity and continuous improvement, leading to higher job satisfaction and employee retention. When employees are empowered to innovate, they feel more engaged and motivated, as they see their ideas being implemented and valued. This culture of innovation also attracts top talent, as professionals are drawn to environments where they can grow and contribute creatively, leading to a more dynamic and fulfilling work environment.
Impact of Innovation
Innovation has a profound impact on various sectors, including business, technology, and the environment.
Business Impact
- Growth and Competitiveness: Innovation is crucial for businesses to stay competitive and grow in a rapidly changing market. Companies like Tesla and Google have revolutionized their respective industries through innovative products and services.
- Job Creation: Innovation can lead to the creation of new jobs, both directly and indirectly, by opening up new markets and industries.
Technological Impact
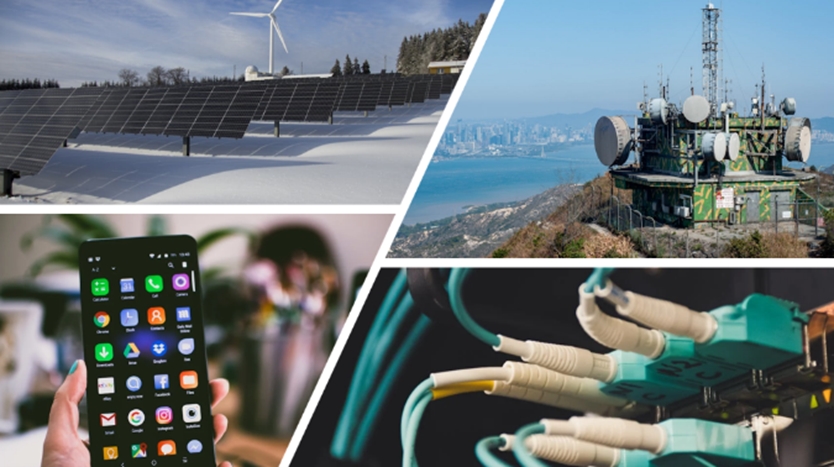
- Digital Transformation: The shift from analog to digital technology has transformed industries such as telecommunications. Digital communication offers improved quality, increased capacity, and enhanced reliability compared to analog systems.
- Mobile Communications: The evolution of mobile technology from 2G to 4G has enabled faster data transmission, higher capacity, and more efficient communication. This has made mobile devices indispensable tools for modern communication.
Environmental Impact
- Renewable Energy: Innovation in the energy sector has made renewable energy sources like solar and wind more competitive. Rapid cost reductions in these technologies have accelerated their adoption globally.
- CO2 Emissions Regulation: In the automotive sector, eco-innovations are incentivized to reduce real-world CO2 emissions. Technologies that provide measurable CO2 savings are rewarded with credits, helping manufacturers meet emissions targets4.
The Energy Market and Innovation
Innovation is driving a significant transformation in the energy market, particularly in the transition to renewable energy sources.
Renewable Energy Technologies
- Solar and Wind Power: Rapid advancements in solar and wind technologies have reduced costs, making them viable alternatives to fossil fuels. This shift is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
- Energy Storage and Grid Flexibility: Innovations in energy storage and grid management are essential for integrating variable renewable energy sources into power systems. This includes developing more flexible power systems to balance supply and demand effectively.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Integration Challenges: The integration of high shares of variable renewable energy poses challenges such as maintaining grid stability and ensuring reliable electricity supply.
- Innovation Solutions: Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions in technology, business models, and market design. This includes smart grids, demand-side management, and new regulatory frameworks to support renewable energy integration.
Regulation of CO2 Emissions
The regulation of CO2 emissions is a critical area where innovation plays a significant role, particularly in the automotive sector.
Eco-Innovations
- Definition and Benefits: Eco-innovations refer to novel technologies that provide real-world CO2 savings beyond standardized test cycles. These innovations are incentivized through regulatory credits, helping manufacturers meet emissions targets.
- Eligibility Criteria: To qualify as eco-innovations, technologies must be novel, contribute to vehicle safety or performance, and demonstrate measurable CO2 savings. They cannot be currently mandated technologies.
Impact on Automotive Industry
- Compliance with Emissions Standards: Eco-innovations help automotive manufacturers comply with stringent CO2 emissions standards. By reducing real-world emissions, these technologies also contribute to environmental sustainability.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Incentivizing eco-innovations can reduce the cost of compliance for manufacturers while increasing overall CO2 reductions.
Technological Shift from Analog to Digital Technology
The transition from analog to digital technology has been transformative, especially in the telecommunications sector.
Advantages of Digital Technology
- Improved Quality: Digital signals offer higher voice and audio quality due to reduced interference.
- Increased Capacity: Digital systems can transmit large volumes of data efficiently, enabling multiple conversations simultaneously.
- Enhanced Reliability: Digital communication provides robust error detection and correction mechanisms, ensuring reliable data transmission5.
Impact on Telecommunications
- Mobile Communications Evolution: The shift from 2G to 4G has enabled faster data transmission, higher capacity, and more efficient communication. This has made mobile devices essential for modern communication.
- Deregulation and Competition: The deregulation of the telecom industry has increased competition, leading to lower consumer rates and a wider range of services.
Deregulation of the Telecom Industry
Deregulation has significantly impacted the telecom industry by promoting competition and innovation.
Historical Context
- Pre-Deregulation: Prior to deregulation, the telecom industry was characterized by monopolies, limiting competition and innovation.
- 1996 Telecommunications Act: This act in the U.S. opened local telephone markets to competition, allowing new entrants and reducing consumer rates.
Effects of Deregulation
- Increased Competition: Deregulation led to increased competition, with new companies entering the market and existing ones expanding their services.
- Innovation and Investment: The competitive environment fostered by deregulation has driven innovation and investment in new technologies and services.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Regulatory Frameworks: Effective regulatory frameworks are crucial to ensure fair competition and protect consumer interests while encouraging innovation.
- Market Growth: Deregulation has positioned the telecom industry for growth, with opportunities for further investment and technological advancements.
Conclusion
Innovation is a critical component of modern business and societal development. Its impact is felt across various sectors, from driving business growth and competitiveness to addressing environmental challenges like climate change. The energy market, CO2 emissions regulation, and the technological shift in mobile communications are all areas where innovation has been transformative. Additionally, the deregulation of the telecom industry has promoted competition and innovation, leading to significant advancements in technology and services. As technology continues to evolve, innovation will remain essential for navigating future challenges and opportunities.